Before you start moving mailboxes you have to make sure that all accepted domains used by mailboxes on-premises are configured in Office 365. This can be tricky, you wouldn’t be the first admin that experience failed migration because of a domain.local email address on an on-premises Mailbox J
Now, when you want to move a mailbox from Exchange on-premises to Exchange Online, navigate again to the Exchange Admin Center, and under recipients select migration. Click the + icon and select migrate to Exchange Online to start the new migration batch wizard.
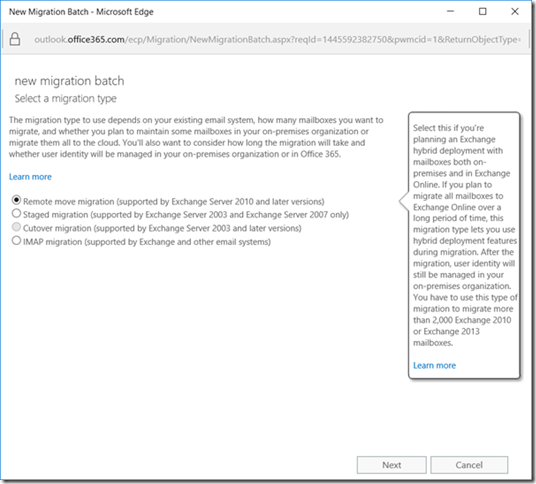
For the migration type, select Remote move migration which is supported by Exchange 2010 or later.
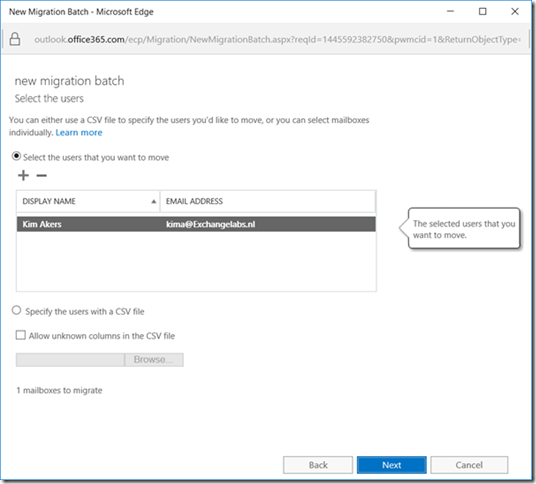
Click Next to continue. Select the mailboxes you want to migrate to Exchange Online, you can use the people picker feature (click the + icon under Select the users that you want to move) for this, or you can use a CSV file to select the mailboxes you want to move.
Continue reading Moving Mailboxes in a Hybrid Configuration – Part II



You must be logged in to post a comment.